How to Build an AI Travel Agent: An End-to-End Guide

According to Deloitte 1 in 10 travelers now use AI for trip planning. The rest are still stuck on airline websites until 3 a.m., comparing prices and reading hotel reviews. Meanwhile, that 10% simply describe what they want and get a ready-made plan. Not a perfect one, such a thing doesn’t exist. But it’s good enough to avoid spending evenings searching for “what if I fly on Wednesday instead of Tuesday?”.
The modern traveler demands a personalized experience. Today, AI is emerging as the revolutionary solution capable of analyzing vast amounts of data, understanding each user’s unique needs, and creating individualized itineraries that were once only accessible through the most experienced travel agents.
We are standing on the brink of a new era in tourism, where the travel AI agent is becoming an intelligent partner in creating unforgettable experiences. Let’s explore how this technology is already transforming the travel industry and what it means for millions of travelers worldwide.
What Is an AI Agent for Travel?
An AI travel agent is not a chatbot with pre-programmed responses. It’s a system that operates like a real human agent: it takes your request, thoroughly analyzes it, uses various tools to search and book, and then returns a ready-made solution.
Look at how it works: a user sends a request through a simple chat interface. The agent receives this information and passes it to a large language model (LLM) like GPT-4, which understands exactly what needs to be done. Next, the system connects the necessary tools – a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system for finding up-to-date information and hotel APIs for booking.
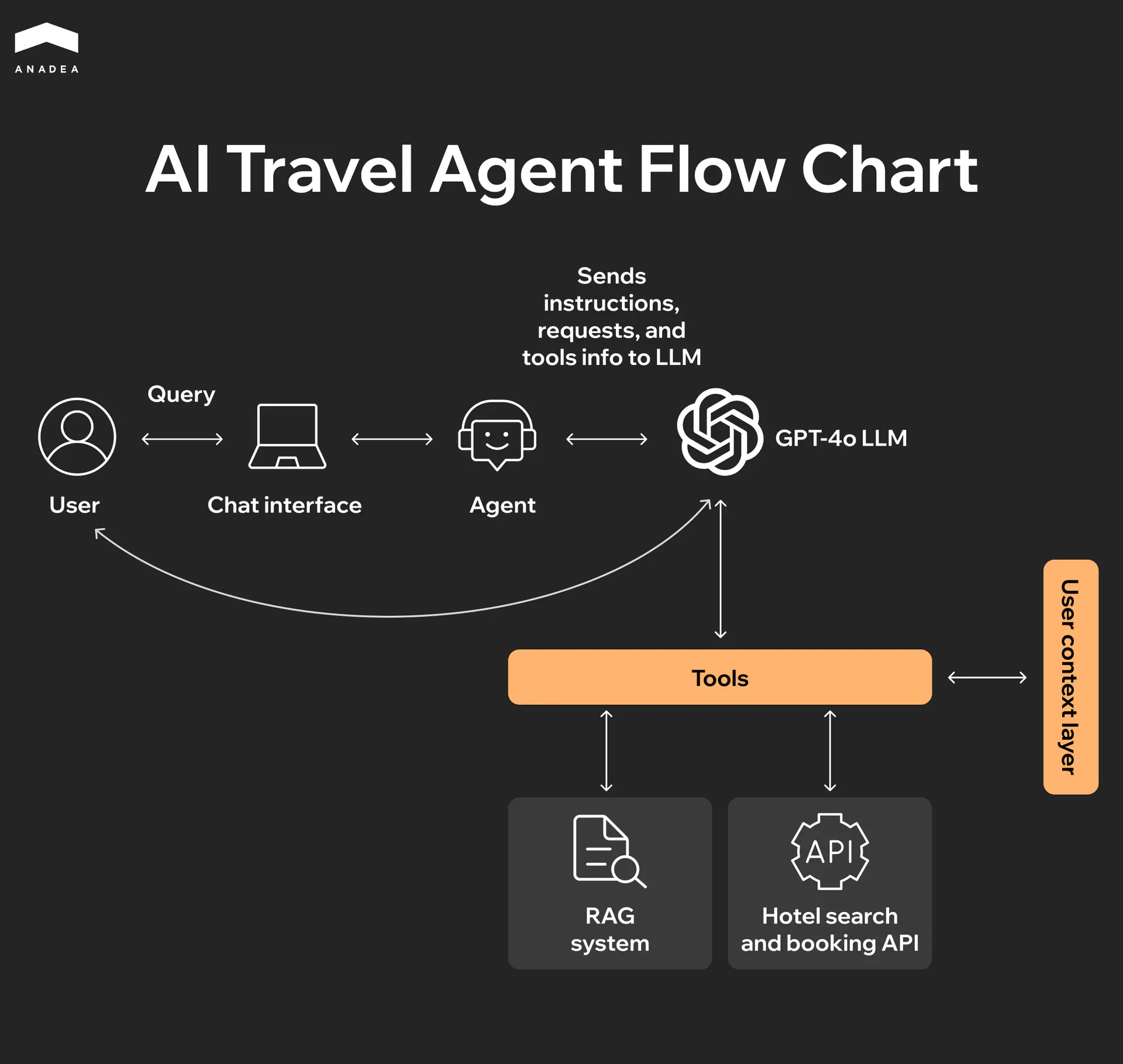
The most critical component here is the Tools. This is what sets an AI travel agent apart from a standard ChatGPT. It can not only converse but also take action: search for flights, check room availability, compare prices in real-time, and book accommodations.
Now, instead of dozens of open browser tabs, your customers can have a single conversation that ends with a concrete travel plan. Not a perfect one, but a functional one. And most importantly – a fast one.
Ready to create your own AI travel agent?
How to Build an AI Powered Travel Agent
Custom AI agent development is our primary focus today.We have dozens of solutions in the pipeline, so we know where the hidden pitfalls lie and are ready to share real-world experience in building a system that works in production.
First and foremost, you must understand that developing an AI agent for travel planning is far more than just integrating ChatGPT with the Booking.com API. It is an architectural challenge that requires a thoughtful strategy, the correct choice of technologies, and, most importantly, a clear understanding of the limitations. Let’s break down our step-by-step approach to such tasks.
Stage 0: Defining the Scope and Core Capabilities (MVP Iteration)
The biggest mistake teams make when starting AI agent development is trying to cover all possible use cases at once. The key question to start with is: What specific problem does your agent solve better than existing solutions?
For the travel domain, we recommend considering the following core capabilities for an MVP:
Conversational Search and Itinerary Planning
This is the core functionality that distinguishes an AI agent from standard search services. The user should be able to formulate a complex request in natural language: “Plan a 5-day trip to Italy focused on art and cuisine, with a budget up to €1200; I dislike large crowds.” The agent must understand all these parameters and generate a personalized itinerary with specific recommendations.
Search and Booking of Core Services
Basic integration with 2-3 reliable APIs for accommodation (Booking.com, Airbnb) and flights (Amadeus, Skyscanner). Important! Do not try to integrate all possible services at once. It’s better to have stable operation with a few providers than unstable operation with dozens.
Contextual Reference Answers
The agent must answer related travel questions: visa requirements, currency exchange rates, weather conditions, local customs, and transport. This creates a sense of a comprehensive service and reduces the user’s need to search for information on other resources.
At the MVP stage, it’s better to perfect 3 functions than to do 10 functions mediocrely. Do not add budget planning, social features, calendar integration, photo recognition, or any other “nice-to-have” features. These can come later if the core product proves viable.
Stage 1: System Architecture (The High-Level Blueprint)
Understanding how to build an AI agent requires a solid architectural blueprint. Once the scope is defined, it’s time to design the architecture. An AI travel agent app is not a monolithic system but an ecosystem of components, each responsible for a specific part of the user experience. Mistakes in the architecture at this stage will be costly later.
The base architecture consists of six key components:
Component | Technologies | Purpose |
Frontend | React/Vue.js, React Native, Telegram Bot API | User interface and entry points |
Backend API | Node.js/Python (FastAPI), API gateway for orchestration | Request processing and coordination of all services |
AI/LLM Core | OpenAI GPT-4, Anthropic Claude, LLaMA | Natural language understanding and response generation |
External APIs | Amadeus, Booking.com, TripAdvisor | Real-time data on flights, hotels, places |
Vector Database | Pinecone, Weaviate, Redis | Semantic search and personalization |
Primary Database | PostgreSQL, MongoDB | Storing user data, bookings, sessions |
1. Frontend Layer
Do not try to create a universal interface. For the MVP stage, one or two channels are sufficient:
- Web Interface. A basic chat with the ability to display maps, images, and structured results.
- Mobile app or messenger bot. For users who plan on the go.
Key requirement: The interface must support complex dialogue, not just simple Q&A.
2. Backend API
This is the orchestrator of the entire system. Its tasks are:
- Accepting user requests and determining intent.
- Coordinating calls to the LLM and external services.
- Managing conversation context and user state.
- Handling errors and fallback scenarios.
Architectural advice: Implement this layer as a microservice with clear API endpoints. This will make it easy to scale and add new features.
3. AI/LLM Core
The choice of model depends on your priorities:
- OpenAI GPT. Best comprehension quality, but expensive and reliant on an API.
- Anthropic Claude. A good alternative with a focus on safety.
- Open-source models (LLaMA, Mistral). Full control, but requires your own infrastructure.
Prompt engineering is a critical aspect. A basic system prompt might look like this:

4. External APIs
Without real-time data, an AI agent is just an intelligent chatbot. Critical integrations include:
- Amadeus API. Flights, hotels, car rentals (professional level).
- Skyscanner API. An alternative for flight search.
- Booking.com API. The largest database of hotels.
- TripAdvisor API. Reviews and ratings.
- Yelp API. Restaurants and local services.
- Wikipedia API. Basic information about places.
- OpenWeatherMap. Weather forecasts.
- ExchangeRate-API. Currency exchange rates.
- REST Countries. Visa requirements and country data.
5. Vector Database
This is what makes your agent “smart” and personal:
- Semantic search through the knowledge base about destinations.
- Personalization based on the user’s previous trips.
- Dialogue context to support complex, multi-step scenarios.
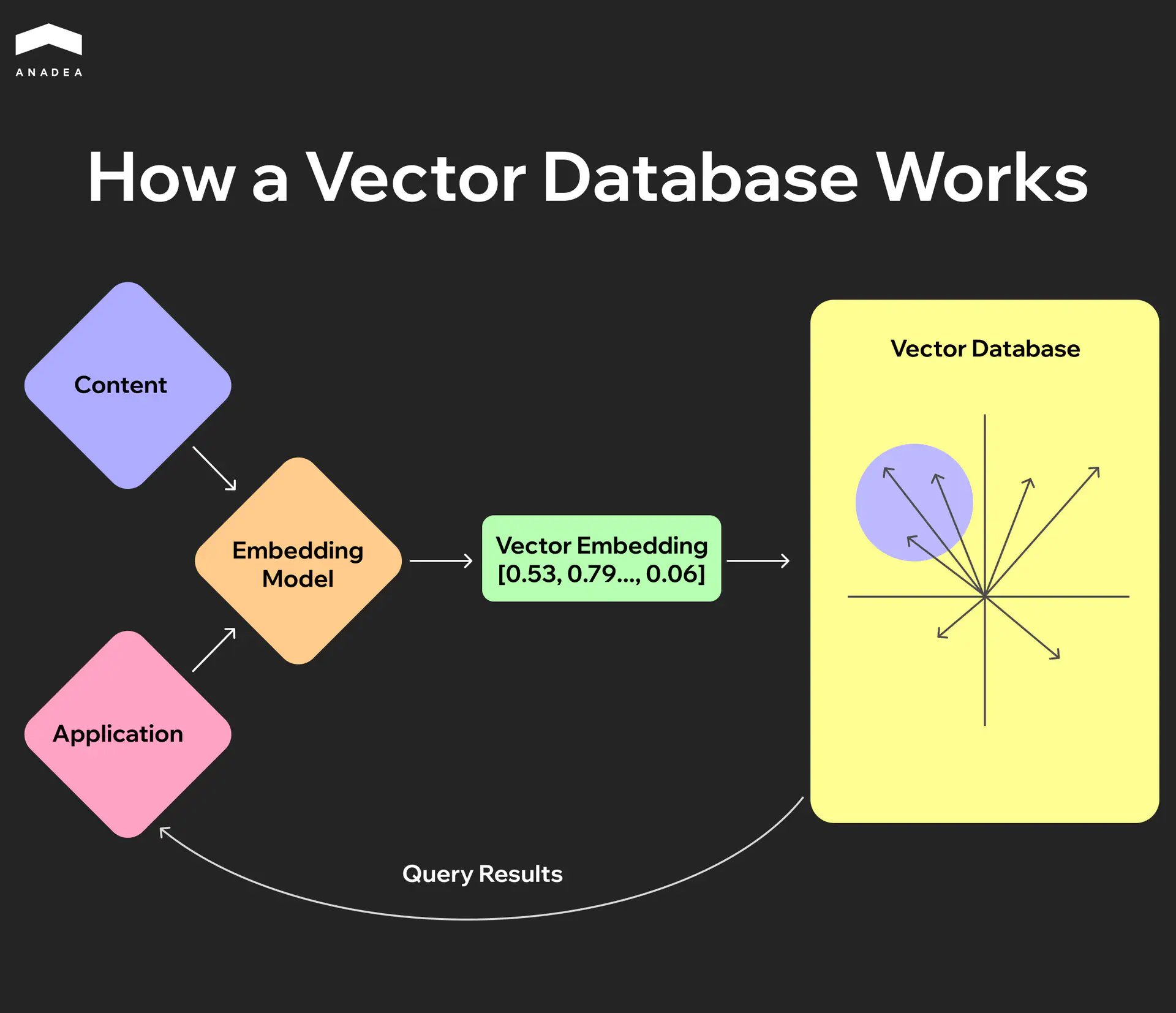
Technology choice depends on scale:
- Pinecone. Managed solution, quick start.
- Weaviate. More control, can be self-hosted.
- Redis with vector search. If you are already using Redis.
6. Primary Database
Stores structured data about users, bookings, and interaction history:
- PostgreSQL. If you need complex relationships and ACID compliance.
- MongoDB. For more flexible data schemas.
Stage 2: AI Model Selection and Configuration
This stage defines the intelligence of your agent. We will focus on three key aspects.
1. Prompt Engineering: Defining Behavior
The foundation is creating a detailed system prompt. It defines the agent’s role (“You are an expert travel planning assistant”), rules of behavior (e.g., to always clarify the budget), and the structure of responses. Use techniques like:
- Few-shot learning. Providing examples within the prompt to teach the model how to handle complex queries.
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT). Breaking down complex reasoning into logical, step-by-step instructions for the model.
2. Fine-Tuning (Optional)
Fine-tuning a model is rarely needed. It is typically reserved for working with unique brand terminology or highly niche knowledge (e.g., gastronomic tourism). For most tasks, sophisticated prompt engineering is sufficient.
3. Tool Calling
This is the most critical technology for converting conversation into real-world actions. An LLM by itself cannot search for tickets. However, it can determine when such a search is needed and call the appropriate function in your backend.
How it works in practice:
- User query. The user asks: “Find me the fastest flight from Lviv to Warsaw next Friday.”
- Your system’s request. Your system sends this query to the LLM (e.g., OpenAI GPT-4) along with a description of the available functions (tools).
- LLM analysis. The model understands that answering requires real-time flight data. Instead of generating a response itself, it returns a structured request to the backend
: {"function": "search_flights", "parameters": {"origin": "LWO", "destination": "WAW", "date": "2024-05-24"}}. - Backend execution. Your server receives this request, calls the external API (e.g., Amadeus), and retrieves a JSON with flight data.
- LLM interpretation. The backend passes the retrieved data back to the LLM, which analyzes it and formulates a human-readable response: “I found three flights for you. The fastest one departs at 14:30, priced at €75.”
Your choice depends on your needs. For a quick start, use a powerful base model (like GPT-4) with thoughtful prompt engineering and be sure to implement tool calling. Reserve fine-tuning for later iterations, once you have a clear understanding of its necessity.
Stage 3: Backend Development and Data Integration (The Nervous System)
For a clearer understanding, let’s recall a school biology lesson. If the AI model is the brain, then the backend is the nervous system that connects it to the “sensory organs” (external APIs) and the “body” (the frontend). At this stage, we create the logic that transforms a user’s request into concrete actions.
1. Creating API Endpoints
Your backend must provide clearly defined API endpoints for request processing. The key ones are:
- POST /api/chat. The main endpoint for dialogue. Accepts the user’s message and conversation context, returns the agent’s response.
- GET /api/trips. For retrieving the history of saved trips.
- POST /api/bookings. For initiating the booking process.
2. Orchestration Layer
This is the most critical component of your backend. It manages a complex workflow. Here is how it works step-by-step:
- The backend receives a request from the frontend (e.g., “Plan a weekend trip to Paris”).
- The request is sent to the LLM along with the system prompt and a description of the available functions (search_hotels, search_tickets, etc.).
- The LLM analyzes the request and determines the necessary actions. For example, the model understands it needs to find tickets and hotels, and returns a command to call the search_trains and search_hotels functions.
- The orchestrator executes the functions. The backend receives the commands from the LLM, calls the corresponding external APIs (in parallel or sequentially), and receives structured data in JSON format.
- The retrieved data is passed back to the LLM. The model now has raw data about flights and hotels.
- The LLM analyzes this data and formulates a human-readable response.
- The backend sends the final response back to the frontend.
Ready to learn what ties all these components together?
Stage 4: Creating the Interface (The Face)
The interface is the point of contact with the user. The main goal is to make interaction with the AI convenient and intuitive.
Key implementation options:
- Chat interface. The most popular and natural option. Ideal for step-by-step planning. For a quick prototype, use Streamlit or Gradio.
- Voice interface. Provides maximum naturalness. Requires integration with speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech (TTS) systems.
Essential UX elements:
- Status indicators. Messages like “Searching for tickets…” or typing animations so the user understands the system is working.
- Error handling. Clear messages such as “I can’t search for hotels right now, please try again in a minute.”
- Context preservation. The agent must remember previous messages within the dialog (e.g., “see the option above”).
Stage 5: Testing, Security, and Deployment
This stage ensures your product’s stability, reliability, and security.
Testing
Functional. Verifying all components work correctly (e.g., does the search API return accurate prices, do function calls trigger properly).
LLM evaluation. A critical phase. Includes:
- Preventing hallucinations. Ensuring the agent doesn’t invent non-existent flights or hotels.
- Response quality. Answers must be useful, relevant, and match the brand’s tone.
- Safety control. Preventing the generation of toxic or inappropriate content.
Security
- Key protection. LLM and external service API keys must be stored in secure vaults (e.g., HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager), not in the code.
- Input validation. Sanitizing all user input to prevent injections (prompt injections, SQL injections).
- Sensitive data handling. Encrypting payment and personal data (PII) according to security standards (e.g., GDPR).
Deployment
- Cloud Infrastructure. Using scalable services from AWS, Google Cloud (GCP), or Azure.
- Containerization. Packaging the application into Docker containers for easy deployment.
- Orchestration. Using Kubernetes for container cluster management, ensuring high availability.
Stage 6: Improvement and Scaling
The product lifecycle continues after launch. The key to success is continuous improvement.
Monitoring and Feedback
- Log analysis. Collecting and analyzing dialogue logs to identify pain points (where users become frustrated).
- A/B testing. Comparing the effectiveness of different prompt versions or even AI models.
Key Technologies for Growth
- RAG. Providing the LLM with fresh data from your knowledge base (e.g., policies, current promotions) for accurate, non-hallucinated answers.
- Personalization. Using vector databases to remember user preferences (e.g., “user prefers quiet beachfront hotels”).
A successful AI agent for travel booking is a living product that constantly evolves with user needs. Technologies change rapidly, but principles remain: user focus, system reliability, and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Building an AI travel agent isn’t about integrating ChatGPT with hotel APIs. It’s about creating an intelligent system that understands human needs and transforms them into concrete solutions. We’ve walked through the journey from defining MVP to scaling, from prompt engineering to production-ready architecture.
The most important insights from our experience:
- Start with limited scope. Better to do three functions excellently than fifteen mediocrely. Users should say “this is more convenient than what I used before” after first use
- Architecture is critically important. An AI agent is not a monolithic system, but an ecosystem of components. Architecture mistakes are expensive at the scaling stage.
- Tool calling is the heart of the system. LLM by itself cannot book hotels. Magic happens when it learns to properly use real tools.
- Security is not optional. API key protection, data validation, confidential information handling – this is not “later,” this is “now.”
- Data makes the difference. A system that learns from every interaction and remembers user preferences transforms from a tool into a partner.
The question isn’t whether AI agents are needed in the travel industry. The question is who will build them first and build them right.
Don't want to miss anything?
Subscribe and get stories like these right into your inbox.
Keep reading

AI-Driven Development: Benefits for Businesses
If you want to enhance your SDLC with the power of AI, explore our guide, in which we talk about the value of AI-driven software development.

Best AI Agents for Healthcare: What You Should Know
If you are looking for a reliable AI agent for healthcare, check our list of the best-rated tools and select a solution that addresses your needs.

How to Create a Marketplace App: Everything You Need to Know
Learn how to create a marketplace app from scratch in this step-by-step guide. Discover essential features, design principles, and tips for a successful launch.
Contact us
Let's explore how our expertise can help you achieve your goals! Drop us a line, and we'll get back to you shortly.