AI in Healthcare Industry: Benefits and Limitations

Not long ago, a doctor may have spent hours analyzing patients’ medical histories, lab results, and diagnostic images to form a complete picture of their health. Now, AI can do the same work in minutes and provide insights for further consideration. And it is only one of numerous AI applications in the healthcare industry.
Today, around 35% of healthcare providers are using AI-driven tools for diagnostic purposes, while 65% of organizations in the industry have started investing in AI training for their employees.
According to the study published by PwC, the AI-related segment of the global healthcare market currently accounts for less than 15%. Nevertheless, by 2030, its share is expected to double. At the same time, Markets and Markets reports that the global AI in healthcare market stood at $14.92 billion in 2024. Experts predicted that by 2030, it will be valued at $110.61 billion, which reflects a CAGR of over 38% for the period from 2025 to 2030.
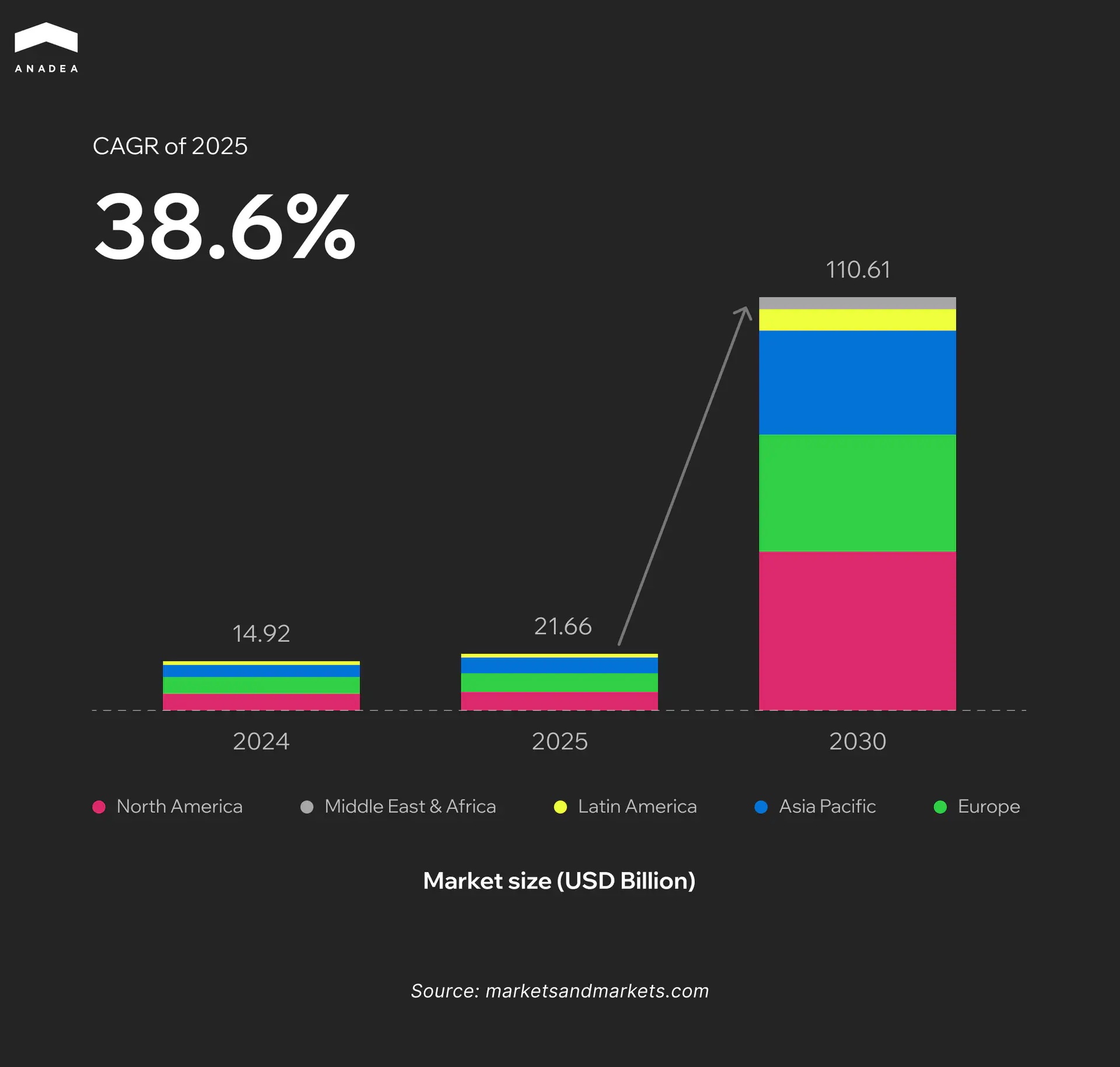
This data highlights the growing role of artificial intelligence in healthcare and the increasing confidence in this technology.
In our article, we will talk about AI applications in healthcare, their benefits, and potential risks. That’s why it will be interesting for those who are planning to build an AI-powered solution for this industry or are just considering this possibility.
What Is AI in Healthcare?
AI in healthcare is the use of advanced algorithms and computational models to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. For example, this technology is often applied to analyze complex data, recognize patterns, flag anomalies, summarize content, and make predictions based on data trends.
Today, the range of AI-driven solutions includes several subfields:
- Machine learning systems. ML algorithms can learn from large datasets, including medical records, collections of diagnostic images, laboratory test results, etc. Based on this, they can detect patterns, identify the earliest signs of diseases, make risk predictions, and forecast treatment responses.
- Natural language processing tools. NLP functionality enables software to understand unstructured text in the human language. As a result, such solutions can analyze and extract insights from physician notes, research papers, and patient records.
- Computer vision. Such tools rely on their image recognition capabilities to interpret medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. They help doctors detect abnormalities with high accuracy.
The first versions of hospital information systems were introduced in the 1960s. Over the decades since their implementation, such traditional systems followed predefined, rule-based instructions. Nevertheless, AI is here to fully change the way healthcare systems can process new data and work with it.
Modern AI-driven medical apps are much better suited for processes where rigid logic is not sufficient. For example, they can cope with such tasks as predicting patient deterioration or suggesting personalized treatments.
AI efficiently processes large datasets, including EHRs, laboratory test results, and population health data. With the actionable insights at their disposal, healthcare providers can significantly enhance the quality of their services, optimize their workflows, and ensure better results for patients.
However, with all these benefits, AI is not introduced to replace doctors. AI systems have another goal. They are designed to support doctors in their work and help them solve tasks where human capabilities are not enough. For example, AI can analyze and summarize patient histories much faster than a doctor can. As a result, when applying reliable AI tools, doctors can focus on complex decision-making and patient care. Meanwhile, actionable insights from patient records will be available to them within seconds.
Looking for a reliable partner to build your AI-powered healthcare solution?
How Is AI Used in Healthcare?
Let’s take a closer look at the domains in healthcare where artificial intelligence can bring real value to both patients and healthcare organizations.
Diagnostics
AI is good at interpreting medical imagery and spotting even the smallest anomalies that may go unnoticed by the human eye. Here are some of the most common use cases.
Over 600 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved AI medical algorithms are in use today, notably 10% of them focus on cardiology. AI helps optimize scan parameters and support early detection. For instance, Apple Watch relied on AI for atrial fibrillation monitoring.
Another example of using AI for disease detection is the technology offered by Google for Health. It developed an AI system that analyzes mammograms to detect breast cancer earlier and with fewer false positives than radiologists. The model behind this solution was trained on thousands of mammograms and can identify complex features that can be signs of cancer.
Predictive Analytics
AI can forecast clinical and population-level health events and trends, including:
- Patient health deterioration and readmissions. ML models can analyze vital signs and EHR data. Based on the analysis, they can anticipate deterioration or readmission risk, which is critical for early medical intervention.
- Epidemic detection. AI can process large datasets to predict epidemic outbreaks and enable proactive resource allocation and containment.
In 2020, it was reported by a range of credible news outlets, including CNBC, that Canadian startup BlueDot identified the COVID-19 outbreak 9 days before official WHO alerts. The startup’s AI-powered platform analyzed global airline ticketing and news reports. Based on this, it detected a cluster of “unusual pneumonia” cases in Wuhan, China.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
AI tools can provide clinicians with evidence-based insights.
One of the tools of this kind, TriageGO, is used by The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, and Howard County General Hospital. The tool utilizes AI to recommend triage acuity levels in emergency departments. This improves patient flow and outcomes under data-scarce conditions.
Virtual Assistants and Symptom Checkers
AI-driven chatbots assist patients with basic guidance and self-assessment, which is especially important in cases when people are waiting for doctor appointments.
Ada is a well-known chatbot that can evaluate symptoms, ask targeted follow-up questions, and provide triage advice. It supports various languages and is particularly helpful for early guidance in rare diseases. Unlike many traditional medical services, Ada is available 24/7 and can help people better understand the reasons for and the ways to relieve any symptoms that can bother them, from anxiety to pain and allergy.
Operational Efficiency
AI solutions in healthcare can also be used to streamline administrative workflows, like claims processing, scheduling, and note-taking. Healthcare organizations can automate such tasks to boost staff productivity, save employees’ time, and improve accuracy.
For example, IBM’s AI agents can be implemented to enhance processes such as optimizing supply chains, streamlining claims management, and automating customer service. In addition to this, AI agents can analyze huge volumes of literature to support doctors in many tasks.
Drug Discovery and Development
Artificial intelligence can be helpful for medical product development and testing.
In 2024, Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs introduced an AI model dubbed AlphaFold 3. The model can predict the structure of proteins, DNA, RNA, and other elements, as well as analyze the potential effect of their interaction.
Meanwhile, Insilico Medicine utilizes AI to design novel drug candidates. The use of this technology can reduce timelines from years to weeks. The company has already initiated human trials for some AI-identified therapeutics. For instance, in August 2025, it became known that the company plans to move its AI-designed Parkinson’s therapy to clinical trials.
Robotics in Surgery and Rehabilitation
AI-powered robots can significantly enhance surgical precision and also support patient recovery.
STAR (Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot) relies on computer vision and machine learning to autonomously conduct surgeries on soft tissues. In 2022, it was reported that the first laparoscopic surgery was successfully performed by a robot without human help.
Apart from this, it’s worth mentioning ReWalk. It provides AI-enhanced exoskeletons that can aid mobility recovery after spinal injuries. These wearable devices combine robotics, sensors, and AI algorithms. Such algorithms can interpret the wearer’s movements and provide real-time assistance for walking and standing. As a result, these devices deliver personalized support and can accelerate rehabilitation.
Benefits of Using AI in Healthcare
As we can see from the AI in healthcare examples, this technology can transform the industry by enhancing not only medical care but also operational efficiency. Here are some of the most important benefits of using AI-powered systems.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, lab results, patient histories, and other data faster and more accurately than traditional methods.
- Increased efficiency. By automating various administrative tasks, healthcare professionals have more time to focus on patient care.
- Personalized medicine. AI enables the development of tailored treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic and clinical data. This approach improves treatment effectiveness.
- Enhanced access in remote areas. Virtual assistants, telemedicine platforms, and AI-based diagnostic tools bring expert medical services to regions with limited access to traditional healthcare organizations.
- Accelerated research and development cycles. AI can model molecular interactions, predict outcomes, and identify promising drug candidates rapidly.
- Lower risks of human error. AI assists clinicians in making decisions related to diagnoses, dosage calculations, and surgical plans. This reduces mistakes that could compromise patient safety.
- Cost reduction. By streamlining workflows, reducing unnecessary tests, and enabling preventive care, AI helps lower healthcare costs.
- Enhanced training and education. AI-powered simulations allow medical students and professionals to practice complex procedures safely and develop new skills.
Challenges of Using AI Solutions in Healthcare
While AI provides a range of benefits for healthcare, its adoption comes with potential obstacles and pitfalls. Based on our practical experience in the implementation of AI solutions in different domains, we can define the most common challenges and the ways to mitigate the associated issues.
What are the key tech challenges in healthcare?
Lack of High-Quality Training Data
AI models need extensive datasets to function effectively across all patient groups. Otherwise, it will be impossible to ensure the inclusion of minority populations.
How to address it:
- Build partnerships between hospitals and research institutes to share anonymized datasets;
- Encourage data standardization;
- Invest in data diversity initiatives.
Interpretability Issues and “Black-Box” Models
A lot of modern AI solutions do not provide any explanation for their outputs. Due to this, clinicians may mistrust AI tools and ignore them in their work.
How to address it:
- Develop explainable AI methods that can offer human-readable reasoning for predictions;
- Combine AI with rule-based systems and confidence scores;
- Offer training sessions for healthcare professionals on how to interpret outputs of AI models.
Resistance to Adoption by Healthcare Staff
AI implementation requires a well-thought-out approach to change management. It is crucial to overcome skepticism and fear of job displacement.
How to address it:
- Involve clinicians in AI system design and testing;
- Clearly explain that AI is expected not to replace but to help medical professionals.
Integration with Legacy Hospital Systems
A lot of healthcare organizations still rely on outdated infrastructures, which makes AI integration complex (and in some cases even impossible).
How to address it:
- Adopt interoperable standards to connect AI with existing EHRs;
- Implement pilot programs in small departments before full-scale implementation to reduce disruptions;
- Introduce cloud-based AI services that reduce the need for on-premises hardware.
You can learn more about the cloud-based product in our article where we discussed the transformative power of healthcare SaaS.
Cost and Infrastructure Barriers in Low-Income Healthcare Organizations
The development and implementation of AI often requires significant investments that are related to extra computing power and hiring skilled staff.
How to address it:
- Develop lightweight AI models that run on basic hardware;
- Leverage open-source solutions to reduce infrastructure costs;
- Introduce government grants to fund AI adoption in underserved areas.
Want to understand how much it will cost to build your solution?
Negative Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
As a rule, the introduction of AI is viewed only from a positive perspective. Nevertheless, we also invite you to consider the risks of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
- Algorithmic bias and unequal treatment. AI models that were trained on non-representative datasets can unintentionally favor certain groups of patients. For example, a lot of currently available diagnostic tools were developed primarily on data from Western hospitals. That’s why they may be less accurate for patients from different ethnic or demographic groups. This can result in health disparities.
- Deskilling of clinicians. AI is increasingly becoming more embedded in diagnostic and treatment workflows. Given this, there is a risk that healthcare professionals may become over-reliant on these tools. With the time flow, their own decision-making skills and clinical judgment can potentially weaken over time.
- Reliability issues in complex cases. AI algorithms demonstrate their highest efficiency when patterns are clear and data is abundant. However, in rare diseases, AI systems may perform poorly. This may lead to misdiagnoses and unreliable recommendations.
- Risk of overdiagnosis and false positives. AI tools can detect anomalies that will be clinically insignificant. This can result in unnecessary testing, patient anxiety, and overtreatment.
- Interruption of the doctor-patient relationship. AI-driven consultations or virtual assistants may depersonalize healthcare. Patients could feel less heard due to the minimization of human interactions.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Ethical Issues
Apart from technical and operational challenges, the rise of AI in healthcare is also associated with significant ethical dilemmas.
- Autonomy and informed consent. Patients have the right to know when AI is being used in their care. Moreover, they need to give informed consent. If AI recommendations are applied without patients fully understanding how their information is processed, this raises ethical concerns.
- Consent for secondary use of data. Quite often, patient data is collected for one purpose, like treatment, but may later be used for research or AI training. It can be done without explicit consent.
- Accountability and liability. When AI makes errors, who is responsible for this? Such uncertainty complicates ethical responsibility in cases of patient harm.
- Equity of access. Advanced AI tools may only be available to well-funded hospitals. As a result, under-resourced or rural areas often don’t have access to such technologies, which widens the healthcare gap between high-income and low-income populations.
Regulatory Landscape and Global Standards for AI in Healthcare
The adoption of AI in healthcare is moving faster than the introduction of the relevant rules and laws that can efficiently regulate the use of this technology. Now, governments and international bodies are actively working to eliminate this regulatory gap and balance innovation with patient safety.
Here is what is happening in this sphere in different regions of the world.
United States
In the US, the introduction and use of AI-driven medical devices are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The FDA is exploring a “Total Product Lifecycle” regulatory approach, which requires AI tools to undergo validation, clinical trials, and post-market monitoring. It is based on the fact that unlike static medical devices, AI-based tools often rely on machine learning models that continuously improve. This creates a challenge for regulators because any change to the algorithm could technically require a new approval.
European Union
The EU has introduced the AI Act, which is the first comprehensive regulation for artificial intelligence all over the globe. It classifies AI systems into several risk categories. The majority of healthcare AI applications fall under “high-risk”. Due to this, such solutions must be rigorously tested. Moreover, human oversight is required before deployment.
Other Regions
Other countries like Canada and Japan are also developing AI-specific healthcare regulations that combine medical device standards with ethical AI frameworks.
For example, the use of AI-powered medical devices in Japan is regulated by the country’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA). It has already approved several AI-based diagnostic tools.
Meanwhile, Health Canada, which oversees medical device regulation in the country, has issued guidance on Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) that covers AI and ML-based tools.
The commonly adopted regulatory approach to AI is the following. To be trusted in clinical settings, any AI-driven solution must be certified like any other medical device. This typically includes:
- Clinical validation;
- Risk management;
- Continuous monitoring.
Explainable AI (xAI)
Moreover, regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing explainability requirements for AI in healthcare.
It means that developers must design systems that provide human-readable explanations of their solutions and the ability to trace a decision back to the data that influenced it.
What are the benefits of explainable AI for the industry?
- Clinicians are more likely to adopt AI tools if they can interpret how decisions are made.
- Transparency helps identify algorithmic biases.
- Explainability is increasingly a legal requirement under laws like the EU’s AI Act.
- Doctors can better explain AI-assisted decisions to patients.
However, regulatory maturity in different countries varies. This represents extra challenges for companies that are working on the deployment of their solutions globally.
Artificial Intelligence Trends in Healthcare: What to Expect in the Near Future?
As AI advances and regulations evolve, new opportunities for healthcare organizations and patients are emerging. The near future will bring new shifts not only in how AI supports clinicians but also in how it ensures transparency and ethics. Below you can find the key trends that are currently shaping the future of AI in healthcare.
- Personalized medicine. It is expected that AI will be increasingly used to enable truly individualized treatment plans. Tailored drug regimens will improve patient outcomes and reduce trial-and-error in therapies.
- AI-powered remote care. Telemedicine will be enriched with AI-driven bots and remote diagnostics. Wearable devices, like smartwatches and biosensors, will leverage AI to detect early warning signs and help manage chronic diseases.
- Growth of predictive and preventive analytics. Health organizations will rely more on AI models to forecast patient deterioration and epidemic outbreaks. This will shift healthcare from reactive treatment to proactive and preventive care.
- Faster clinical trials. AI models will be used to accelerate molecule discovery, simulate drug interactions, and optimize clinical trial recruitment. This will help ensure faster time-to-market for critical medications.
- Focus on federated learning. Healthcare institutions will invest in systems powered by federated learning. This approach allows organizations to collaboratively train AI models without sharing their raw data. It will help them meet strict privacy regulations.
Wrapping Up
AI is reshaping the healthcare industry. Developers can build powerful tools for various use cases, such as diagnostics, predictive analytics, personalized treatments, and administrative efficiency. The adoption of such solutions has undeniable practical value. But it also comes with significant challenges, like data privacy risks and ethical dilemmas.
As healthcare organizations are increasingly implementing AI in their processes, we can expect to see more personalized and efficient care provided to patients worldwide.
To achieve the desired results, organizations should not only know ethical and regulatory guidelines but also have a reliable technology partner, like Anadea, who understands both AI and the nuances of the medical field.
Our company was founded more than 25 years ago, and since then, we have been actively accumulating expertise in various domains, including healthcare. Our specialists deeply understand the pain points of this industry and know how to address them with the power of such innovative technologies as AI and ML.
To learn more about our experience and services, contact us, and we will find the right approach to solving your tasks.
Have questions?
- No, AI is not intended to replace doctors. Instead, it is introduced as a support system to help doctors analyze information more quickly and accurately. While AI can suggest possible diagnoses or treatments, people remain responsible for clinical judgment and empathy. Only doctors can make final decisions in patient care.
- Explainable AI (XAI) is a term used to describe AI systems that can show how they reached the provided outcomes. In healthcare, the role of such systems can’t be underestimated. Doctors and patients must understand why an AI tool suggested a diagnosis or treatment. It helps build trust and support regulatory compliance.
- Today, AI is commonly applied to interpret X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and other medical images. AI models often detect conditions earlier than human specialists. For instance, AI tools can flag early-stage cancer signs and help reduce diagnostic errors.
Don't want to miss anything?
Subscribe and get stories like these right into your inbox.
Keep reading

AI in Remote Patient Monitoring: Use Cases and Benefits
How does AI assist in remote patient monitoring? Find an answer in our blog post where we talk about the key AI use cases and share practical tips.

Best AI Agents for Healthcare: What You Should Know
If you are looking for a reliable AI agent for healthcare, check our list of the best-rated tools and select a solution that addresses your needs.

Image Recognition in Healthcare: How AI Is Transforming Medical Diagnostics
Explore how image recognition in healthcare improves diagnostics across radiology, pathology, and ophthalmology. Learn where AI delivers real results and how to build your own solution.
Contact us
Let's explore how our expertise can help you achieve your goals! Drop us a line, and we'll get back to you shortly.