Core Web Vitals: What They Are & How to Improve Them
In May 2020 after Google’s update of the algorithm a lot of sites lost their positions and traffic, because they were not prepared. To prepare your site for the Core Web Vitals update you need to improve it right now! To calculate all the changes you make with your site Google needs at least one month (if you have enough traffic there).
And to make your site faster and better it takes a lot of time, so if you start now all actions will take at least 2 months and remember Google’s update is just around the corner. If you want to SEO optimize your site, let's take a look at what Core Web Vitals are, how to measure them and where to find metrics, as well as some tips and free tools to improve your site's Core Web Vitals.
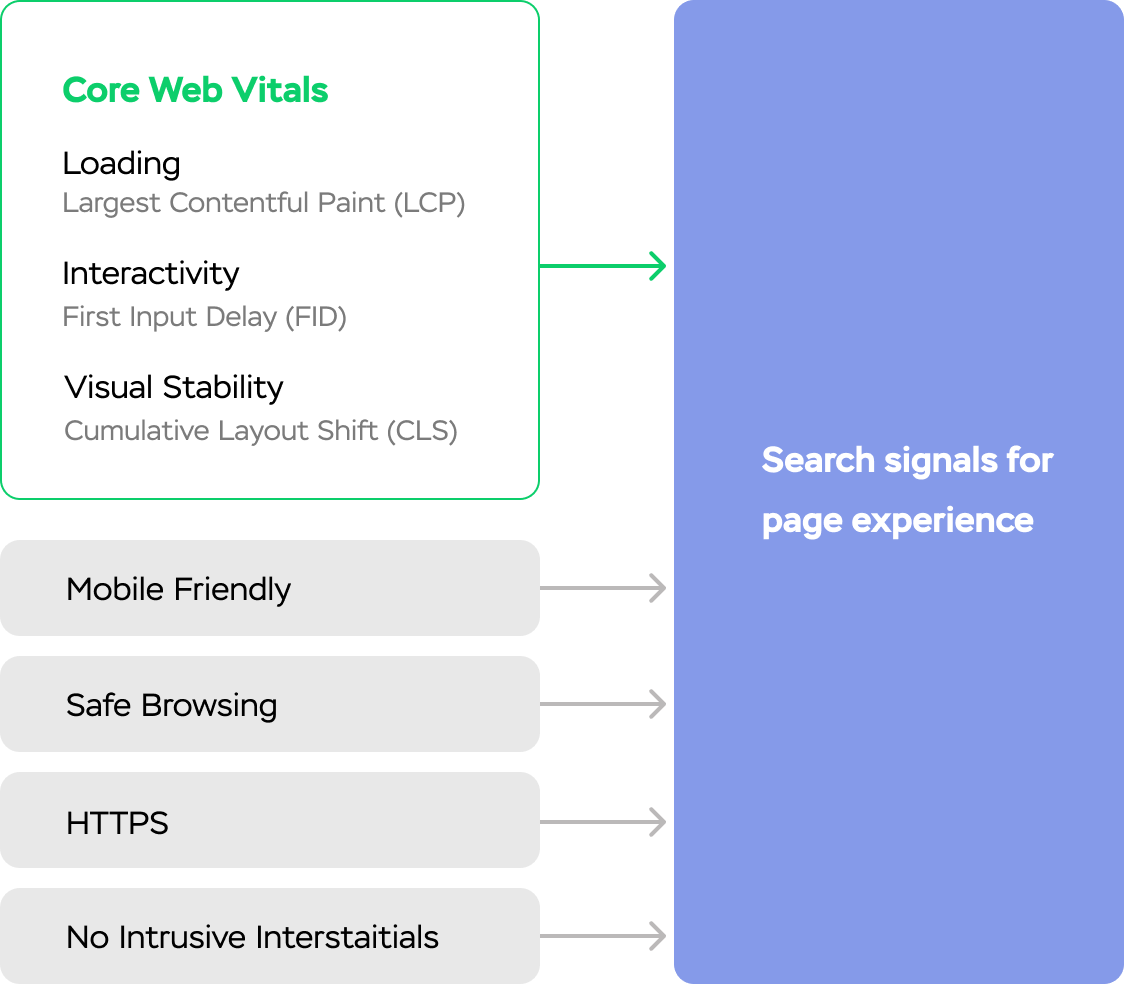
Core Web Vitals is the algorithm from Google that can calculate t he main factors that could affect the user experience. Google has identified three main web vitals of user experience:
-
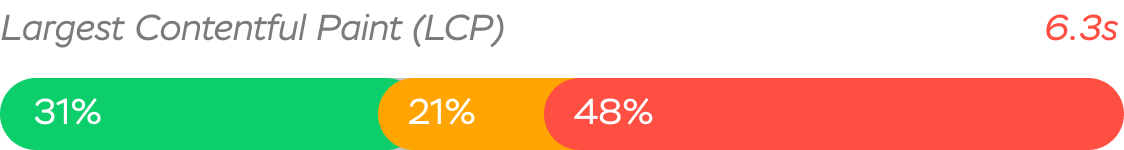
Loading - Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
-
Interactivity - First Input Delay (FID)
-
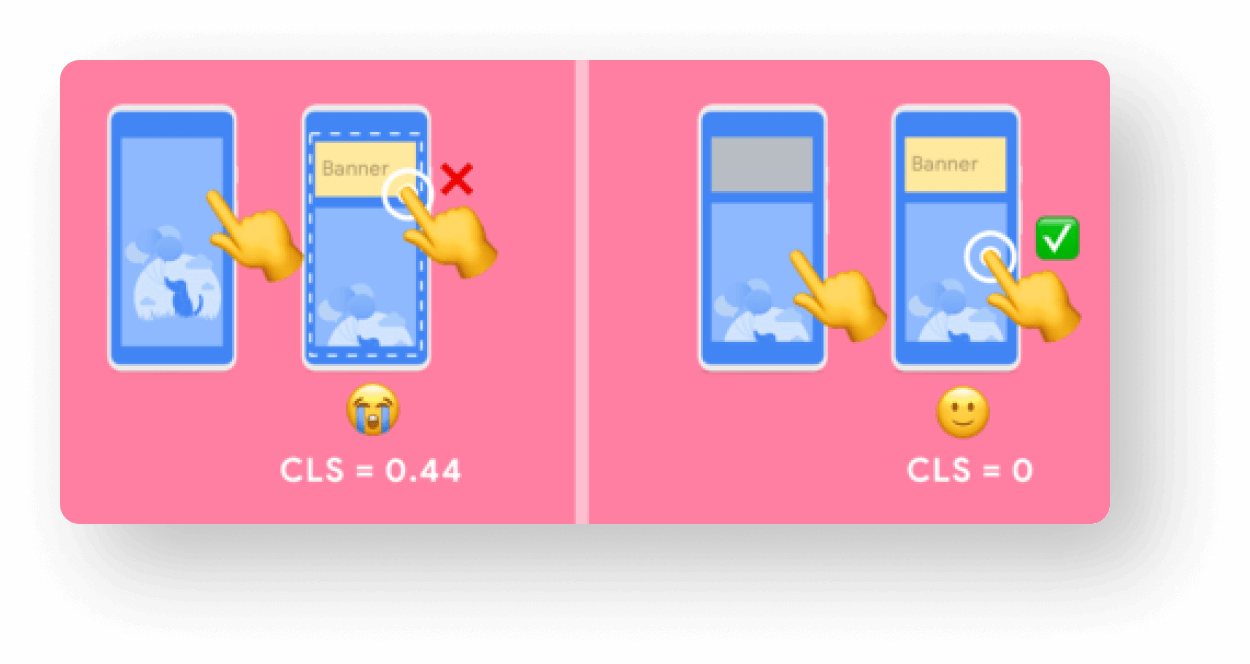
Visual stability - Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
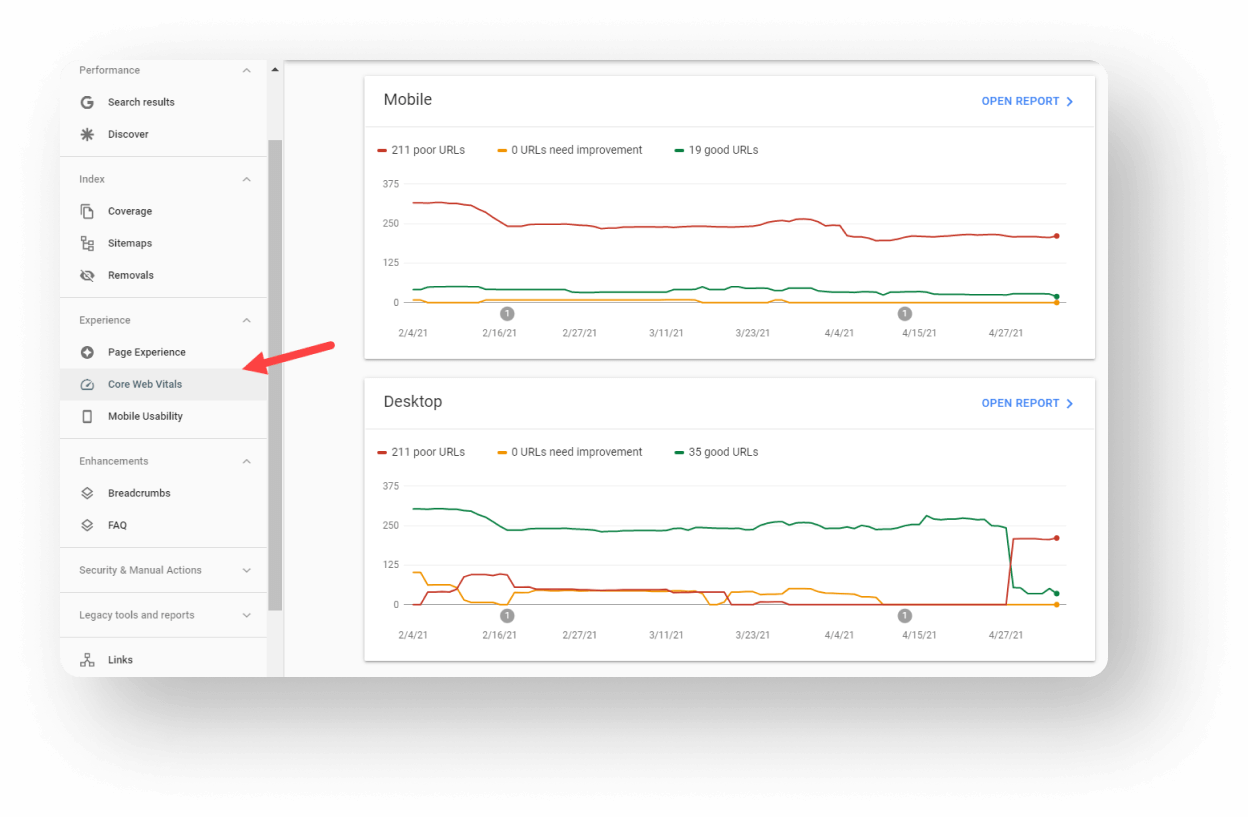
These Core Web Vitals are a part of Google’s “User experience” score. You can find Core Web Vitals of your site in the Google Search Console. There you can find 2 reports: For Mobile and For Desktop.
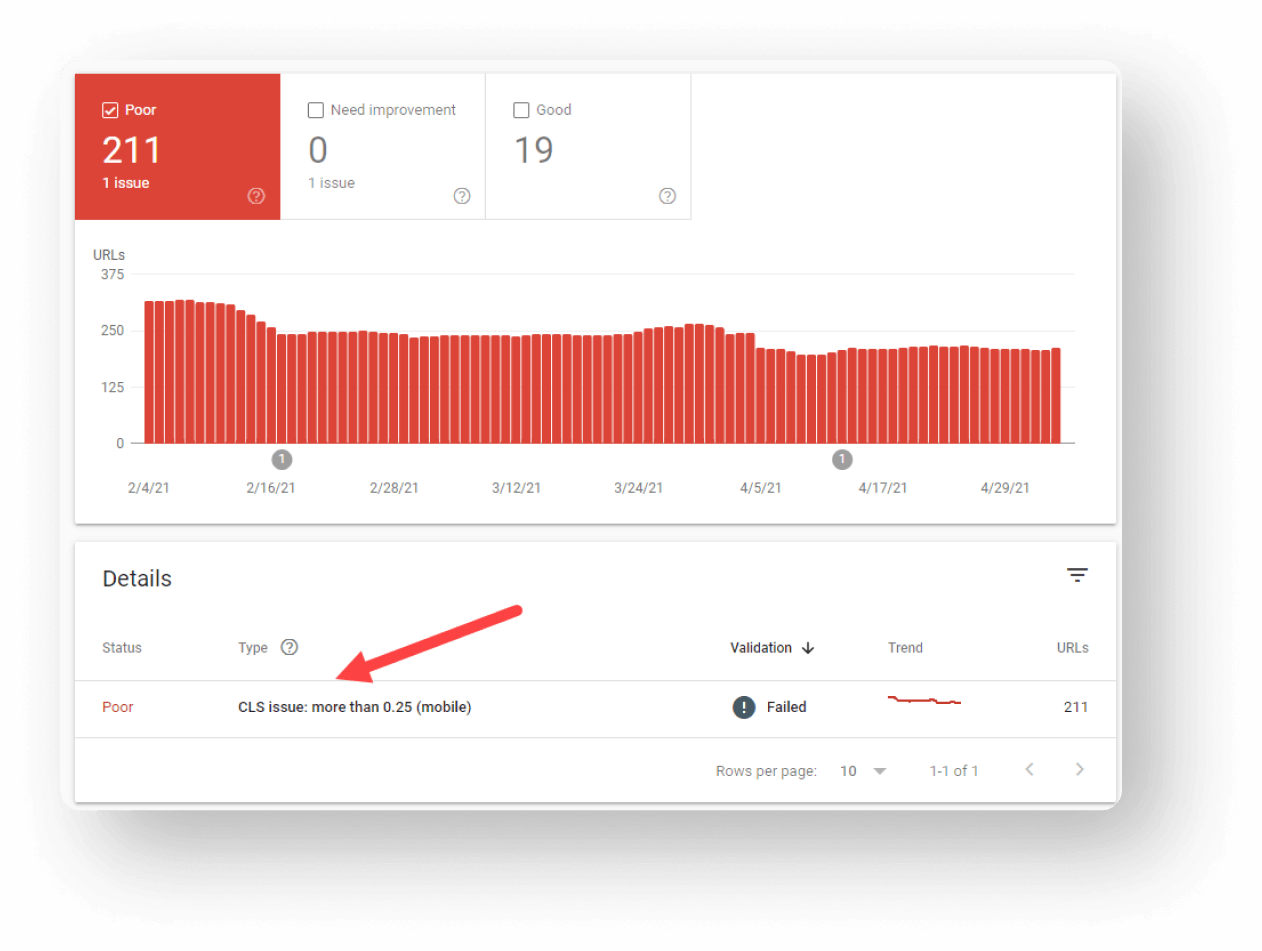
If you want to find what kind of problem your pages have, then you should click on the “Open Report” and then you will see the problems with the score you need to improve.
-
Loading - Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
-
Interactivity - First Input Delay (FID)
-
Visual stability - Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
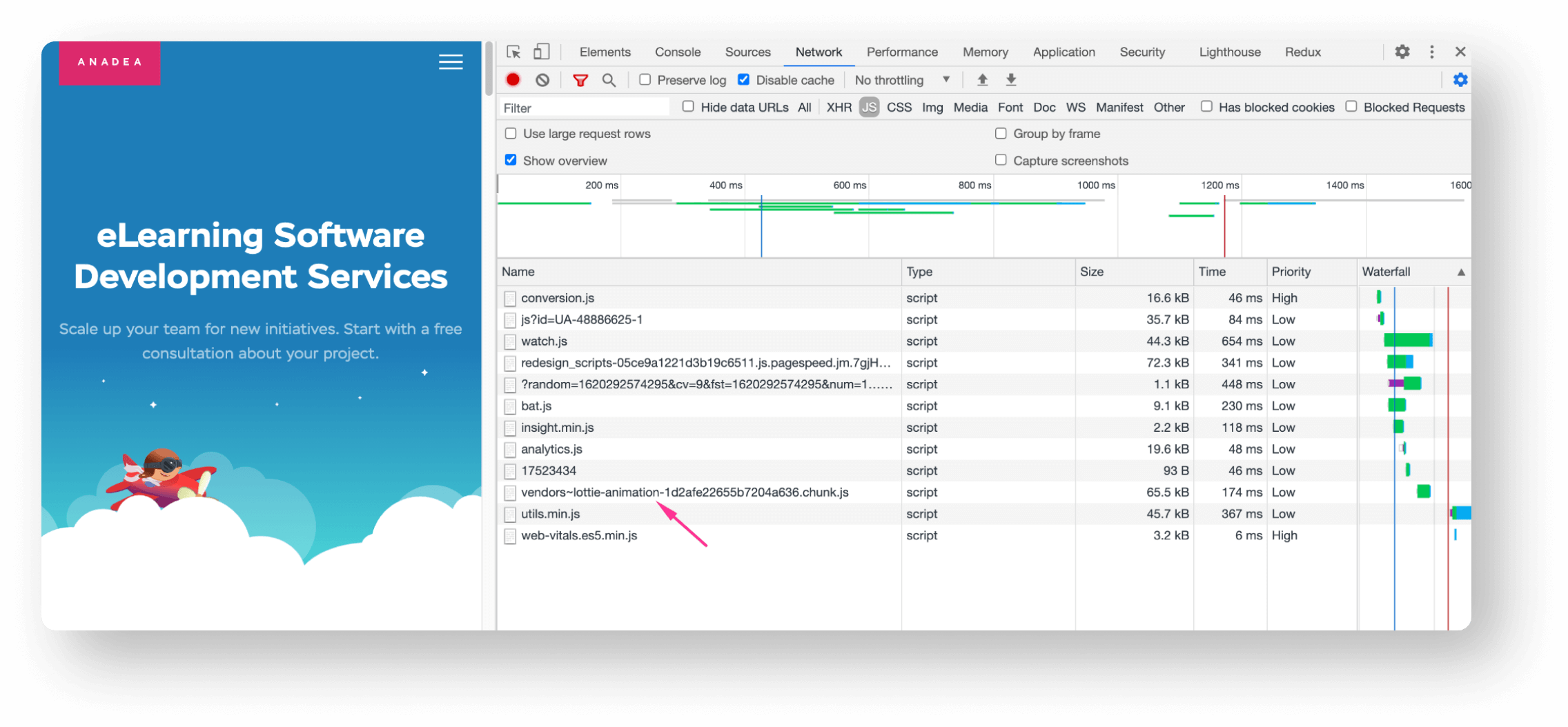
-
Slow server response times
-
Render-blocking JavaScript and CSS
-
Slow resource load times
-
Client-side rendering
-
Clicking on option from a menu
-
Clicking on a link in the site’s navigation
-
Entering your email into a field
-
Opening “burger” menu on the mobile phone

-
Minimize (or defer) JavaScript
-
Remove any non-critical third-party scripts
-
Use a browser cache

-
Use set size attribute dimensions for any media
-
Make sure ads elements have a reserved space
-
Add new UI elements below the fold